এই লেখাটি একটু বেশি বেসিক লেভেলদের জন্য।
আপনি যদি একটু এডভান্স লেভেলের হয়ে থাকেন, তাহলে দয়া করে লেখাটা ইগনোর করুন।
তবে এটা এমন একটা লেখা হতে যাচ্ছে; প্রতিজন অ্যাফিলিয়েট মার্কেটারের এই বিষয়গুলো জানা বাধ্যতামূলক। আপনার ইনভেস্টমেন্ট বেশি আছে? সবকিছু আউটসোর্স করে অ্যাফিলিয়েট মার্কেটিং করতে চান? নিজে বসে থাকবেন; আর আপনার নিস সাইটের যাবতীয় কাজ ওয়ার্কাররা করে দেবে?
জ্বি, আপনি থামুন!
নিস সাইট দুনিয়া থেকে সরে যান এখুনি। এই দিন আর নেই ভাইয়ারা, আপুরা। নিস সাইট এমন একটা ব্যাপার, এখানে সাকসেস পেতে হলে বিষয়টাকে আপনার অউন করতে হবে। ভূমিকা শেষ, চলুন মূল কথা শুরু করি।

গুগল র্যাংকিং ফ্যাক্টর কি?
গুগল একটা সার্চ ইঞ্জিন। এরকম আরও অনেকগুলো সার্চ ইঞ্জিন অনলাইন জগতে আছে। কিন্তু গুগল এমন একটা অবস্থায় পৌঁছে গেছে, যার ফলে আমরা সার্চ ইঞ্জিন বলতে মূলত গুগলকেই বুঝি। ব্যাপারটা অনেকটা আমাদের দেশের “আমার বাংলালিংক নাম্বারে বিশ টাকার ফ্লেক্সিলোড করে দেন” কিংবা “এই রকেট নাম্বারে দুই হাজার টাকা বিকাশ করা যাবে ভাই?” কথার মতো হয়ে গেছে।
তো যাইহোক, আমরা এখানে গুগলের কথাই বলছি। বলতেই থাকবো আর বলতেই হবে। গুগল র্যাংকিং ফ্যাক্টরটাকে যদি সহজ ভাষায় সংজ্ঞা দিই তাহলে এরকম দাঁড়ায়: কোনো কিছু দরকার হলে আমরা যখন গুগলে সার্চ করি, সেখানে ঐ দরকারি বিষয়টার অনেকগুলো রেজাল্ট আমরা দেখতে পাই। কোনোটা প্রথম পেজে আবার কোনোটা হাজার পৃষ্ঠা পরে দেখায়।
কেন?
কারণ, এই দেখানোর পেছনে কিছু ব্যাপার কাজ করে। এই ব্যাপারগুলোই র্যাংকিং ফ্যাক্টর। বিষয়টা অনেকটা ক্লাসে একজন ছাত্র প্রথম হয় আরেকজন লাস্ট হওয়ার মতো। যে প্রথম হয়, সে প্রত্যেকটা বিষয়ে ভালো নম্বর পায়। যে লাস্ট হয় সে প্রত্যেকটা বিষয়েই খারাপ করে। হয়তো দুয়েকটা বিষয়ে ফেইলও করে।
সুতরাং যে যে বিষয়গুলোর জন্য গুগলের সার্চ রেজাল্টে একটা ওয়েবসাইটকে প্রথমে দেখায় এবং অন্যটাকে অনেক পরে দেখায়; সেই বিষয়গুলোকেই আমরা বলবো র্যাংকিং ফ্যাক্টর।
এই বিষয়গুলো কি কি? এগুলোই আমরা জানবো এই লেখায়।
গুগলের র্যাংকিং ফ্যাক্টর কি কি?
গুগলের অ্যালগরিদম অনুযায়ী ২০০+ র্যাংকিং ফ্যাক্টর এক্সিস্ট; বর্তমান জামানায়। এগুলো নিয়ে সবচেয়ে বেশি এবং প্রমাণিত তথ্য এসেছে ব্রায়ান ডিনের এই লেখায়। মূলত ব্রায়ানের এই দীর্ঘ আর্টিক্যালের সূত্র ধরেই আমার এই লেখা সাজিয়েছি। তবে আমার লেখায় সবগুলো ফ্যাক্টর নেবো না। মিনিমাইজ করে নিয়েছি আমি। শুধুমাত্র যেগুলো আমার নিস সাইটে এপ্লাই করেছি এবং ফলাফল ভালো পেয়েছি সেগুলোই এখানে লিস্ট করবো।
এর মূল কারণ হচ্ছে- এই ২০০+ র্যাংকিং ফ্যাক্টরের সবগুলোই কিন্তু কার্যকরী নয়। এগুলোর কিছু আছে প্রমাণিত (আমি এগুলোর উপরেই জোর দেবো), কিছু আছে সাংঘর্ষিক, আর কয়েকটা আছে যেগুলো নিয়ে কোনো এসইও এক্সপার্টই কিছু বলতে পারেননি। ধারণা করা হচ্ছে সেগুলো ডেড বা মৃত; অর্থাৎ কোনো ভূমিকাই এখন নেই ওগুলোর।
তাছাড়া, ব্রায়ানের লেখায় দেখবেন কিছু ব্যাপার পুনরাবৃত্তি বা একই কথা ঘুরেফিরে একটু অন্যরকম করে বলা হয়েছে। আমি মনে করি ওগুলো জেনে মাথা ভারি করার কোনো দরকার নেই।
সুতরাং বুঝতেই পারছেন এখানে ২০০+ র্যাংকিং ফ্যাক্টরের সবগুলো নিয়ে আলোচনা করা হচ্ছে না। কারণ আমি মনে করি সবগুলো দরকার নেই। যারা সবগুলোই জানতে চান, তারা দয়া করে ব্রায়ানের লেখাটা পড়ে নিতে পারেন। আমার এক সময়ের চিন্তা ছিলো যেন আমি চোখ বন্ধ করে এই ২০০+ র্যাংকিং ফ্যাক্টর মুখস্ত মনে করতে পারি। তাই করেছিলাম। যদিও এটা ছিলো আবেগের বাড়াবাড়ি, কিন্তু আমার মনে হয়, গুগলের র্যাংকিং ফ্যাক্টরগুলো ভালো করে জানা থাকলে এসইও’র ৯০% বিষয় জানা হয়ে যায়।
যাইহোক, শুধুমাত্র প্রয়োজনীয় গুগল র্যাংকিং ফ্যাক্টরগুলো এখানে আলোচনা করতে যাচ্ছি আমার নিজস্ব মতামতসহ। আশা করছি এগুলোই যদি আপনি ভালো করে জানেন, তাহলে একটা নিস সাইট সহজেই আপনি র্যাংক করতে পারবেন। মুখস্ত কোনো কাজ করতে হবে না। মোটা দাগে গুগল র্যাংকিং ফ্যাক্টরগুলো হচ্ছে:
- ডোমেইন সংক্রান্ত
- ওয়েবসাইট ভিজিবিলিটি সংক্রান্ত
- ব্যাকলিংক সংক্রান্ত
- অডিয়েন্সের অ্যাঙ্গেজমেন্ট সংক্রান্ত
- গুগলের স্পেশাল অ্যালগরিদম
- ব্রান্ড্যাবিলিটি ভিজিবল
- অনপেজ সংক্রান্ত
- অফপেজ সংক্রান্ত
তাহলে চলুন, কথা না বাড়িয়ে পয়েন্ট-বাই-পয়েন্ট শুরু করা যাক।
“আপনি যদি এসইও, অ্যাফিলিয়েট মার্কেটিং, নিস সাইট তৈরি… ইত্যাদি শিখতে চান, তাহলে অথোরিটি এইড ইউটিউব চ্যানেলটি দেখতে পারেন।”
১। ডোমেইনের বয়স
বেশির ভাগ এসইও এক্সপার্ট মনে করেন, একটা নিস সাইটের ডোমেইন এইজ যতো বেশি হয়, সেটা পজেটিভ ফ্যাক্টর হিসেবে কাজ করে। কিন্তু গুগলের আগের প্রধান ম্যাট কাটস এই বিষয়টাকে গুরুত্বহীন বলে আখ্যায়িত করেছেন।
তার মতে একটা পুরনো ডোমেইন এবং নতুন ডোমেইনের মধ্যে তেমন কোনো তফাৎ নেই। এটা বড় কোনো ইস্যু নয় বলেও তিনি মতামত দিয়েছেন।
আমার ব্যক্তিগত অভিজ্ঞতা ম্যাটের বলা কথার সাথে মিলে। হ্যাঁ, এ কথা বলার অপেক্ষা রাখে না যে, একটা ওল্ড ডোমেইন যদি পারফেক্ট ম্যাট্রিকসের হয়, তাহলে নিঃসন্দেহে সেটা নিয়ে কাজ করা পজেটিভ। কিন্তু সমস্যা হলো, “পারফেক্ট” সেটা বুঝবেন কী করে? বিশেষ করে একজন নতুন নিস সাইট মার্কেটারের জন্য ভুল করাটাই স্বাভাবিক। দ্বিতীয় ব্যাপার হলো- একটা পারফেক্ট ওল্ড ডোমেইনের দাম ৫০০ ডলার মিনিমাম। আমাদের কমিউনিটিরই অনেক ভাই-ব্রাদার ২/৩ হাজার ডলার দামের ডোমেইন নিয়ে কাজ করেন/করতে দেখেছি। অথচ একজন নতুন মার্কেটারের সর্বসাকুল্যে ইনভেস্টই থাকে ম্যাক্সিমাম এতো। সুতরাং ভালো মানের ওল্ড ডোমেইন নিয়ে নতুন মার্কেটারের কাজ করা সাজে না, সম্ভবও নয়।
তাই, ডোমেইনের বয়স সংক্রান্ত র্যাংকিং ফ্যাক্টর নিয়ে একজন নতুন মার্কেটারের মাথা ঘামানোর কোনো দরকার নেই। নতুন মার্কেটাররা সরাসরি নতুন ডোমেইন নিয়ে কাজ করবেন। তবে খেয়াল রাখতে হবে, নতুন ডোমেইন সবসময় নতুন হয় না। মানে এটা যেন ড্রপড ডোমেইন না হয়, সেদিকে কঠোর নজর রাখতে হবে।
একটা নিস সাইটের জন্য সহজে কীভাবে ডোমেইন সিলেক্ট করবেন, নির্ভুলভাবে; জানার জন্য নিচের ছোট্ট ভিডিওটা এক পলকে দেখে নিতে পারেন।
২। ডোমেইনে কীওয়ার্ড
দিন কয়েক আগেই এই বিষয়টা কনট্রোভার্সারি ছিলো। কিন্তু এখন এটা কনফার্ম। ডোমেইনে কীওয়ার্ডের ব্যাপারটায় দুটো ব্যাপার আছে- ফুল কীওয়ার্ড থাকা এবং কীওয়ার্ডটা ডোমেইনের শুরুতে থাকা। উদাহরণ দিচ্ছি:
ধরুন আপনার কীওয়ার্ড হচ্ছে best egg plant, এখন আপনার ডোমেইন এরকম হতে পারে:
- BestEggPlant.com
- theBestEggPlant.com
- EggPlant.com
- BestEggPlantReviews.com
- BestEggPlants.com
যাইহোক না কেন, এক কথায় উপরের সবগুলোই ভুল। যা-ই করতে যান না কেন, এটা হবে আপনার ভুল সিদ্ধান্ত। তাহলে এ ক্ষেত্রে ডোমেইনের নাম কেমন হতে পারে?
আমার দৃষ্টিতে নিচের পদ্ধতিতে যদি আপনি ডোমেইন কিনেন তাহলে হবে সবচেয়ে গুড প্রাকটিস:
- EggMaker.com
- EggWorld.com
- EggLovers.com
- EggAid.com
এমনকি অনেক এসইও এক্সপার্ট কীওয়ার্ড দিয়ে সাব-ডোমেইন তৈরি করেও সাইটকে স্ট্রং করে থাকেন। আমি ২০১১ সালে একজন ক্লায়েন্টের জন্য এরকম একটা কাজ করেছিলাম। তার মেইন ডোমেইনের জন্য প্রায় ১০০+ সাব ডোমেইন বানিয়ে ওয়ার্ডপ্রেস সেটাপ দিয়ে সাইট বানিয়ে দিয়েছিলাম। কিন্তু আমার কাছে মনে হয় ওটা একটা ওল্ড স্কুল টেকনিক। এখন আর এগুলোর ভ্যালু নেই। সুতরাং আমি আমার রিডারদের বলবো এরকম ফ্যাক্টরকেও এড়িয়ে চলার জন্য।
৩। ডোমেইনের ক্যারেক্টার লেংথ
ওয়েল, এবার পেয়েছি। হাহাহাহ! আমার কাছে মনে হয় এটা একটা গুরুত্বপূর্ণ ব্যাপার। ডোমেইন কত ক্যারেক্টারের হবে এটা একটা বড় বিষয়। আমি উদাহরণ হিসেবে 10beasts.com দেখাতে পারি; ডোমেইনের দৈর্ঘ্য কম এবং সফল নিস সাইট। আপনি হয়তো অনেক বড় দৈর্ঘ্যের সফল নিস সাইট দেখাতে পারেন। কিন্তু আমার ব্যক্তিগত অভিজ্ঞতা হচ্ছে- ডোমেইনের ক্যারেক্টার লেংথ যতো কম হয়, এসইও’র জন্য সেটা ততো ভালো।
আমার যে সাইটটা সর্বশেষ ফ্লিপ করেছি, ওটা নাইন ক্যারেক্টারের একটা ডোমেইন ছিলো। মিনিমাম সাত এবং ম্যাক্সিমাম ১৩ ক্যারেক্টারের ডোমেইন আমি ব্যবহার করি আমার নিস সাইটের জন্য। আমার কাছে এটা অত্যন্ত গুরুত্বপূর্ণ একটা ফ্যাক্টর মনে হয়। সুতরাং চাইলে আপনি এটা ফলো করে দেখতে পারেন।
৪। ডোমেইনের ইতিহাস
ইতোমধ্যে এই বিষয়টা নিয়ে বলে ফেলেছি। তাছাড়া উপরের ভিডিওটা দেখলে আরও ক্লিয়ার বুঝতে পারবেন ডোমেইনের ইতিহাস কতটা জরুরি। ব্যাপারটা হলো এই: ধরুন আপনি বাজেটের অভাবে কিংবা ওল্ড ডোমেইন চিনতে পারবেন না তাই নতুন ডোমেইন রেজিস্ট্রেশন করে কাজ শুরু করলেন।
কিন্তু কয়দিন পর দেখলেন- ইজি কীওয়ার্ড, ভালো মানের আর্টিক্যাল, স্ট্রং ব্যাকলিংক করার পরেও সাইট অল্প একটু আগানোর পর পেনাল্টি খেয়ে গেছে।
আপনি জানেন এই পেনাল্টির কারণ কী?
কারণ হচ্ছে- ডোমেইনটা নিয়ে আগে কেউ একজন কাজ করেছিলেন। তারপর ওটা পেনালাইজড, স্প্যামিং হয়ে যাওয়ার পর সে বাদ দিয়েছে। নিয়মানুযায়ী ডোমেইনটা নির্দিষ্ট সময় পর নতুন করে রেজিস্ট্রেশনের উপযোগী হয়েছে। আর আপনি ভাবলেন এটা আগে কেউ কিনেনি, মানে নতুন; তাই কিনলেন।
কিন্তু আদতে ব্যাপারটা তা নয়। এই বিষয়টা বুঝবেন কীভাবে? এই টিউটোরিয়ালে এটা জানতে পারবেন।
৫। অ্যাক্সাক্ট ম্যাচ ডোমেইন – পারশিয়াল ম্যাচ ডোমেইন
ডোমেইন সেকশনে এটা বলা হয়ে গেছে অলরেডি। কিন্তু যেহেতু এই দুটো বিষয়ই এড়িয়ে চলবেন, তাই আবারও বলছি। আপনার কীওয়ার্ড যা, তাই যদি হয় ডোমেইনের নাম; তাহলে সেটা ইএমডি বা অ্যাক্সাক্ট ম্যাচ ডোমেইন, আর কীওয়ার্ডের সাথে সামান্য মিল রেখে ডোমেইন হলে সেটা পিএমডি বা পারশিয়াল ম্যাচ ডোমেইন। ধরুন আপনার কীওয়ার্ড best egg plant। তাহলে:
ইএমডি হবে: BestEggPlant.com
পিএমডি হবে : EggPlant.com
এর কোনোটাই ব্যবহার করা যাবে না। একদম নয়।
৬। ডোমেইন হুইজ গার্ড
বেশিরভাগ ডোমেইন রেজিস্ট্রার হুইজ ফ্রি দিয়ে থাকে। যার কারণে আমরা প্রায় সবাই-ই হুইজ গার্ড বা প্রোটেকশন ইউজ করি।
ডোমেইন হুইজ গার্ড বা প্রোটেকশন কাকে বলে?
একটা ডোমেইন একজন ব্যক্তি বা প্রতিষ্ঠানের নামে নিবন্ধন করতে হয়। হুইজ-এর মাধ্যমে জানা যায় সেই ব্যক্তি বা প্রতিষ্ঠানের নাম। কিন্তু অনেকে সেটা হাইড করে রাখেন। ফলে প্রকৃত মালিকের নাম জানা যায় না। এটাই ডোমেইন হুজি গার্ড বা প্রোটেকশন।
এখন কথা হলো, এটা করবেন, নাকি করবেন না? ম্যাট কাটসসহ অনেক এসইও এক্সপার্টের মতে হুইজ গার্ড বা প্রোটেকশন ব্যবহার করার ফলে একটা ওয়েবসাইট পেনাল্টি পর্যন্ত খেতে পারে বা খায়।
কেন?
যদি কোনো কারণে প্রকৃত মালিকের নাম জানা যায় এবং দেখা যায় সে বা তার আইপি ইন্টারনেট জগতে স্প্যামের তালিকায় রয়েছে, তাহলে ঐ সাইটটা পেনাল্টি খায়।
তাহলে কি আমরা হুইজ প্রোটেকশন ব্যবহার করবো না?
এটা আপ-টু য়ু। কারণ, যদি, না-ও করেন তাহলেও কিন্তু আপনি ধরা খাবেন যদি কালো তালিকায় আপনার নাম থাকে। এই জন্য ডোমেইন কেনার সাথে সাথেই হুইজ গার্ড এনাবল করে ফেলা ভালো। তাহলে আর প্রকৃত মালিকের নাম কোথাও রেকর্ড হতে পারবে না।
ব্যক্তিগতভাবে আমি আমার নিস সাইটের ডোমেইনের জন্য হুইজ গার্ড ব্যবহার করি। যেহেতু আমি নেইমচিপ বা নেইমসিলো থেকে ডোমেইন কিনি, আর তারা ফ্রি হুইজ গার্ড প্রোভাইড করে; সুতরাং ডোমেইন কেনার সময়েই হুইজ গার্ড এনাবল করে দিই। ইদানিং সবচেয়ে কম দামে এক্সনহোস্ট ফ্রি হুইজ গার্ডসহ ডোমেইন বিক্রি করছে। সুতরাং চাইলে তাদের কাছ থেকেও নিতে পারেন।
না, ডোমেইন তাদের কাছ থেকে কিনলে কমিশন পাবো না আমি 😉 । তবে হোস্টিং কিনলে জানায়েন। স্পেশাল ডিসকাউন্ট লিংক (যা শুধুমাত্র অথোরিটি এইড রিডারদের জন্য বরাদ্দ) দিতে পারবো আর সেই লিংক থেকে কিনলে আপনিও বড় একটা ডিসকাউন্ট পাবেন, আর আমিও ছোট একটা বোনাস পাবো। হাহাহা!
৭। ডোমেইন এক্সটেনশন
একটা কমন প্রশ্ন সবার- ভাই, ডট কম ছাড়া অন্য কিছু নিয়ে কাজ করলে কি সমস্যা? এক কথায় উত্তর হচ্ছে: সমস্যা না। তবে ডট ইনফো ডোমেইন নিয়ে কাজ না করতে পরামর্শ দেবো। এছাড়া যেকোনো এক্সটেনশন ডোমেইন নিয়েই কাজ করতে পারেন।
গুগলের পক্ষ থেকে ক্লিয়ার বলা আছে, এক্সটেনশন কোনো ম্যাটার না। কিন্তু এখন ব্যাপার হলো- আপনার নিস সাইটের টার্গেট অডিয়েন্স হচ্ছে ইউনাইটেড স্টেটস অব আমেরিকা, আর আপনি যদি ডট কম ডট বিডি কিংবা ডট কম ডট ইউকে নিয়ে কাজ করেন তাহলে সেটা কেমন দেখায় না?
হুম, ভাই, এই কমনসেন্সটা কাজে লাগাতে পারলে আর সমস্যা হবে না। তবে ব্যক্তিগতভাবে আমি পরামর্শ দেবো ডট কম ডোমেইন এক্সটেনশন নিয়ে কাজ করার জন্য। সুনির্দিষ্ট কোনো লজিক নেই। কিন্তু এখনও বেশিরভাগ মানুষ ওয়েবসাইট বলতে মূলত ডট কম এক্সটেনশনকেই বুঝায়। আর সেটা খোদ আমেরিকাতে আরও বেশি। সুতরাং বুঝতেই পারছেন।
৮। কীওয়ার্ডের ব্যবহার
একটা নিস সাইটের জন্য আমরা যেসব কীওয়ার্ড নিয়ে কাজ করি সেগুলো নানানভাবে বিভিন্ন জায়গায় ব্যবহার করি বা করতে হয়। যেমন আর্টিক্যালের টাইটেল ট্যাগে, আর্টিক্যালের ভেতরে, বিশেষ করে প্রথম প্যারাগ্রাফে, এইচ-ট্যাগে, আর্টিক্যালে ডেনসিটি… এগুলো কাউন্ট করা বা ব্যবহার করা কতটা জরুরি?
বেশিরভাগ এসইও এক্সপার্ট মনে করেন এগুলো ওল্ড স্কুল টেকনিক। বর্তমান সময়ে এগুলোকে গুরুত্ব দেয়ার কিছু নেই। কারণ গুগল যদি বুঝতে পারে বিষয়টা কোনোভাবে আরোপিত, তাহলে পেনাল্টি দিতে কসুর করবে না। সুতরাং বিষয়টা রয়েসয়ে-চিন্তা-ভাবনা করে করা উচিত।
তবে আমার ব্যক্তিগত মতামত হচ্ছে- টাইটেল ট্যাগের শুরুতে সম্ভব হলে কীওয়ার্ড ব্যবহার করা উচিত। আর ব্যবহার করতে পারেন আর্টিক্যালের শুরুতে। তবে প্রথম প্যারাগ্রাফেই হতে হবে; এমন নয়। আর আর্টিক্যালের ভেতরে একবারও যদি ব্যবহার না করেন, সমস্যা নেই। ওভারঅল অপটিমাইজ করা সুখপাঠ্য আর্টিক্যাল হলেই সেটা ভালো আর্টিক্যাল।
৯। কনটেন্ট লেংথ
অত্যন্ত গুরুত্বপূর্ণ একটা র্যাংকিং ফ্যাক্টর। দেখা গেছে একজন মাত্র এক হাজার ওয়ার্ড আর্টিক্যাল দিয়ে কীওয়ার্ড র্যাংক করে বসে আছেন। আরেকজন তিন হাজার ওয়ার্ড আর্টিক্যাল দিয়েও নিজের কীওয়ার্ড র্যাংক করাতে পারছেন না?
এর কারণ কী?
কমন এই প্রশ্নের উত্তরটা খুবই সোজা। তারপরও বেশিরভাগ নিউবি এই প্রশ্নটা করেন: ভাই, কত ওয়ার্ডের আর্টিক্যাল দেবো?
আপনি নিজেই এই প্রশ্নটার উত্তর দিতে পারবেন। অন্য কেউ পারবে না। কারণ হলোা, আপনি আপনার সাইটের নিস এবং কীওয়ার্ড রিসার্চ করেছেন। উত্তরটা তখুনি পেয়ে গেছেন আপনি। খেয়াল করে দেখেন, আপনার কীওয়ার্ডে গুগলের প্রথম পৃষ্ঠায় সব থেকে বেশি কার আর্টিক্যালের লেংথ? কিংবা আপনার কমপিটিটরের আর্টিক্যাল লেংথ কত? সবচেয়ে যারটা বেশি, তারটা থেকে যেন আপনার আর্টিক্যালের লেংথ বেশি হয়।
তবে এখানে একটা বিষয় লক্ষ্যণীয়, যদি দেখেন, ঐ কীওয়ার্ড দিয়ে গুগলের প্রথম পেজের ম্যাক্সিমাম সাইট-ই অনেক বেশি ওয়ার্ড দিয়েছে (যেমন সবারই হয়তো ৪/৫ হাজার ওয়ার্ড), তাহলে আমি বলবো, আপনি সুপার এক্সপার্ট না হলে এই কীওয়ার্ডটা এড়িয়ে যান।
সুতরাং বুঝতেই পারছেন, কেন একজন এক হাজার ওয়ার্ড দিয়ে র্যাংক করে ফেলতে পারেন আর আরেকজন কেন তিন হাজার ওয়ার্ড দিয়েও পারেন না? কারণ তিনি কমপিটিটর ভালো করে রিসার্চ করেন নি। করলে দেখতে পেতেন, তার কমপিটিটর আরও বেশি ওয়ার্ডের আর্টিক্যাল দিয়ে বসে আছেন।
ব্যক্তিগতভাবে আমি আমার নিস সাইটের মানি আর্টিক্যালের জন্য ১৭৫০ থেকে ৫০০০ ওয়ার্ড ব্যবহার করি। দুয়েকটা ব্যতিক্রম আছে। আর ইনফো আর্টিক্যাল ৫৫০ থেকে ১২৫০ ওয়ার্ড যথেষ্ট মনে করি।
সংবিধিবদ্ধ সতর্কীকরণ: আর্টিক্যাল কোয়ালিটি হিসেব না করে যদি শুধুমাত্র লেংথ হিসেব করেন, তাহলে একটা মারাত্মক ভুল হবে। সুতরাং বি কেয়ারফুল!
১০। টেবিল অব কনটেন্টস
এসইও নিয়ে কাজ করেন, এরকম প্রায় সব এক্সপার্টই মনে করেন টিওসি বা টেবিল অব কনটেন্টস একটা গুরুত্বপূর্ণ র্যাংকিং ফ্যাক্টর। কারণ হচ্ছে, টিওসি একটা আর্টিক্যালে থাকার অর্থ হচ্ছে- ঐ আর্টিক্যালটা একজন রিডার খুব সহজে নেভিগেট করতে পারবেন। আর অডিয়েন্সের কাছে বিষয়টা যতো সহজভাবে আসবে, তারা ততো বেশি আপনার সাইটে অ্যাঙ্গেজ হবেন। আর যতো বেশি অ্যাঙ্গেজ করাতে পারবেন, গুগল ভাই আপনার সাইটকে ততো বেশি ‘লাভ’ করবে।
সুতরাং বুঝতেই পারছেন, টিওসির গুরুত্ব কতটা বেশি। তবে প্রসঙ্গত বলি, ব্যক্তিগতভাবে আমি কোনো প্লাগিন ইউজ করে টিওসি ব্যবহার করি না; আর্টিক্যালে। একদম ম্যানুয়ালভাবে তৈরি করে ইউজ করি। আপনি চাইলে সেটা করতে পারেন।

১১। কীওয়ার্ড ডেনজিটি
নতুনদের এটা একটা কমন প্রশ্ন: একটা আর্টিক্যালে মেইন কীওয়ার্ড কতবার ব্যবহার করা হবে? আমার মনে হয় ফেসবুক ইনবক্সে আমি কয়েকশ’ বার এই প্রশ্নটার উত্তর দিয়েছি। একটা সময় ছিলো যখন যতো বেশি মেইন কীওয়ার্ড আর্টিক্যালে দেয়া হবে ততই ভালো। এখন গুগলে এরকম আর্টিক্যালকে বলে থিন আর্টিক্যাল, স্প্যাম আর্টিক্যাল। ভাবা যায় ইগ্লা! হাহাহাহা। এনিওয়ে, আসলেই তাই। আপনার রাইটার আর্টিক্যালে মানি কীওয়ার্ড কীভাবে ব্যবহার করেছে সেটা দিয়েও খুব সহজে বুঝা যায় ঐ রাইটারের কোয়ালিটি। যদি দেখেন জোর করে আর্টিক্যালে মানি কীওয়ার্ড ঢুকানো হয়েছে, খুব সহজেই ঐ রাইটারের ক্যাপাবিলিটি বুঝে যাবেন।
তাহলে কীওয়ার্ড ডেনজিটি কত হবে?
১%?
৩%?
০.৫%
আমার উত্তর হচ্ছে কোনোটাই না। আমার উত্তর মানে, বর্তমানের এসইও এক্সপার্টদের কথা বলছি আর কি! বর্তমান সময়ে গুগল যে গেম খেলতেছে, সেটা জানলে অবাক হবেন। উপরেও বলেছি বোধহয়: একটা মেইন কীওয়ার্ড একটা আর্টিক্যালে নাই, তাও ঐ কীওয়ার্ড দিয়ে আর্টিক্যালটা র্যাংক হয়ে আছে।
কেন?
কারণ বর্তমান সময়টায় গুগল এআইয়ের উপর প্রচণ্ড জোর দিচ্ছে। গুগলের বট খুব সহজেই একটা আর্টিক্যালের কোয়ালিটি বুঝতে পারে। কেন একটা কীওয়ার্ড একটা আর্টিক্যালে না থাকার পরও সেটা র্যাংক হয়, তা জানতে হলে আপনাকে বুঝতে হবে র্যাংক ব্রেইন মেথড সম্পর্কে।
১২। এলএসআই কীওয়ার্ডস
এটাকে অনেকে লংটেইল কীওয়ার্ডও বলে থাকেন। কিংবা কীওয়ার্ড ভ্যারিয়েশনও বলতে পারেন। একটা কীওয়ার্ড কত রকমভাবে ব্যবহার করা যায় এটা জানা একজন অ্যাফিলিয়েট মার্কেটারের কর্তব্যই বলা চলে। আর একজন রাইটারের মুন্সিয়ানা তখনই ভালোভাবে বুঝা যাবে যে, উনি কী পরিমাণ এলএসআই কীওয়ার্ড ব্যবহার করেছেন আর্টিক্যালে।
সুতরাং ওভারঅল বুঝতেই পারছেন, এলএসআই বা লং টেইল কীওয়ার্ডের গুরুত্বটা। অনেকে মেটা ডেসক্রিপশনে এবং টাইটেলে এলএসআই ব্যবহার করে; সরাসরি মূল কীওয়ার্ড না দিয়ে। আমার কাছে এটা গুড প্রাকটিস মনে হয় না। এখনও আমি টাইটেল এবং মেটাতে মেইন কীওয়ার্ডই ইউজ করি। আপনি পরীক্ষা-নিরীক্ষা করতে চাইলে সেটা ভিন্ন কথা।
১৩। আর্টিক্যালের গভীরতা
র্যাংক ব্রেইন মেথডটা ভালো করে পড়লে বুঝতে পারবেন, বর্তমান সময়ে গুগল কত বেশি গুরুত্ব দিয়ে থাকে আর্টিক্যালের উপর। ধরুন, আপনার আর্টিক্যালে যদি কোনো সমস্যা থাকে, যতো চেষ্টাই করেন না কেন, সাময়িক র্যাংক হওয়ার পর খুব শিগগিরিই র্যাংক ড্রপ হয়ে যাবে। এবং সেসব আর্টিক্যাল আর র্যাংকে ফিরিয়ে আনতে পারবেন না। সাধারণত আনা যায় না। যদি না আপনার সুপার দখল থাকে এসইওতে।
সুতরাং কখনোই সস্তা ধরে আর্টিক্যাল নিয়ে নিজের ক্ষতি করতে যাবেন না। অবশ্য এটাও সত্যি যে, সস্তা মানেই যে মন্দ; তা নয়। কিন্তু সেটা আপনাকে বুঝতে হবে।

১৪। ওয়েবসাইট লোডিং স্পিড
র্যাংকিং ফ্যাক্টরের আরেকটা গুরুত্বপূর্ণ বিষয় আপনার ওয়েবসাইটের লোডিং স্পিড। গুগল এই বিষয়টা প্রায় ক্লিয়ার করে দিয়েছে যে, লোডিং স্পিডের উপর র্যাংক নির্ভর করে।
এখন একটা গুরুত্বপূর্ণ বিষয় হচ্ছে: অনেকেরই একটা কমন ধারণা আছে যে, দামি এবং ভালো হোস্টিং সার্ভিস হলেই বুঝি সাইটের লোডিং স্পিড ভালো হয়। তাদের জ্ঞাতার্থে জানাচ্ছি: এটা সম্পূর্ণই একটা ভুল ধারণা।
তাহলে কি হোস্টিংয়ের উপর সাইটের লোডিং স্পিড নির্ভর করে না?
অবশ্যই করে। কিন্তু লোডিং স্পিডটা শুধুমাত্র হোস্টিংয়ের উপরই নির্ভর করে না। দেয়ার আর সামথিং এলস। কী সেটা? সেটা হচ্ছে: সাইট কতটা অপটিমাইজ করা হয়েছে সেটার উপরেও সাইটের লোডিং স্পিড নির্ভর করে।
সুতরাং দামি আর ভালো মানের হোস্টিং কিনেই আপনার কাজ শেষ নয়। আর্টিক্যাল যেমন অপটিমাইজ করার ফলে এর ক্ষমতা বেড়ে যায়; ওয়েবসাইটের স্পিড অপটিমাইজ করার ফলেও সাইটের ক্ষমতা বেড়ে যায়। দ্রুত লোড হয়। সুতরাং সবসময় এই দু’টো বিষয়ের দিকে নজর রাখতে হবে সাইটের লোডিং স্পিড বাড়ানোর জন্য।
আর সবসময় মনে রাখবেন, সাইটের লোডিং স্পিড বাড়ার ফলে ঐ সাইটের র্যাংকে দ্রুত পজেটিভ ইমপ্যাক্ট পড়ে।
১৫। ইমেজ অপটিমাইজেশন
আরেকটা গুরুত্বপূর্ণ র্যাংকিং ফ্যাক্টর। ইমেজ নিয়ে নতুন মার্কেটারের মধ্যে এতো এতো কনফিউশন যা বলার বাইরে। আমি এমনও নিস ওয়েবসাইট দেখেছি, যেগুলোতে সরাসরি গুগল থেকে ইমেজ নিয়ে এসে সাইটে বসিয়ে দেয়া হয়েছে। এমনকি ইমেজের নামটাও পাল্টানো হয়নি। আর খুব কম ব্যক্তিই আছেন যারা অল্টার ট্যাগ ব্যবহার করেন ইমেজের জন্য।
অথচ এটা খুবই জরুরি। ইমেজ অপটিমাইজের জন্য কি কি করতে হবে? প্রথমে যেকোনো একটা এডিটর দিয়ে ইমেজটা এডিট করে রিসাইজ করে ওয়েব ফরমেট বা জেপিইজি বা পিএনজিতে নিয়ে নেবেন। তারপর ইমেজের প্রোপার্টিজ থেকে নিচের বিষয়গুলো ঠিক করে নেবেন:
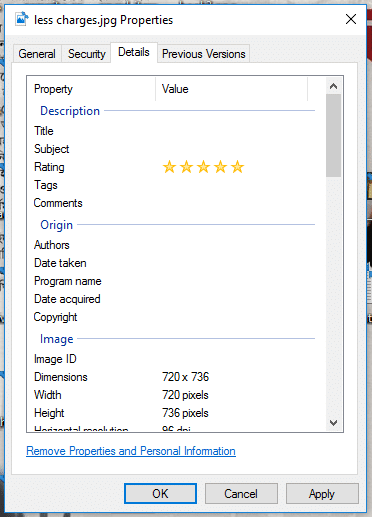
— ইমেজ টাইটেল
— ইমেজের রেটিং
— অউনার চেঞ্জ করা
আর তারপর দ্বিতীয় কাজ হচ্ছে: সাইটে আপলোড করে সঠিক অল্টার ট্যাগ দেয়া। এভাবে ইমেজ ব্যবহার না করার অর্থ হচ্ছে, গুগলকে বৃদ্ধাঙ্গুলি দেখানো। যা গুগল কোনোভাবেই পজেটিভ হিসেবে নেয় না।
যারা পেইড ইমেজ ব্যবহার করতে চান না, তারা গুগল ইমেজ থেকে যদি ইমেজ নেন তাহলে যথোপযুক্ত অনুমতিযুক্ত ইমেজগুলো নেবেন। অথবা এসব সাইট থেকে ইমেজ নিয়ে নিজের স্বাধীনমতো ব্যবহার করতে পারেন। কোনোরকম ক্রেডিটও দিতে হবে না: ফ্রি ইমেজেস, পেক্সেলস, পিক্সাবে।
১৬। এইচ ট্যাগ
এইচ ট্যাগ নিয়ে আমি একটা দীর্ঘ আর্টিক্যাল লিখেছি। ওটা পড়ে নিতে পারেন এখান থেকে। আশা করি এইচ ট্যাগ নিয়ে আপনার আর কোনো সমস্যা থাকবে না। যেহেতু গুগলের র্যাংকিং ফ্যাক্টরে এটা একটা ভূমিকা রাখে, সুতরাং এর ব্যাবহারটা জানা জরুরি।
দ্বিতীয় ব্যাপার হলো, এইচ ট্যাগের যথাযথ ব্যবহারের ফলে আর্টিক্যালের স্ট্রাকচার/ডিজাইন বেশ সুন্দর হয়। এই বিষয়টা তাই গুরুত্বের সাথে ফলো করা উচিত।
১৭। আউটবাউন্ড লিংক কোয়ালিটি
একটা আর্টিক্যাল থেকে আউটবাউন্ড লিংক দেয়া যেমন পজেটিভ ব্যাপার (চমৎকার একটা রিলিভেন্সি তৈরি হয় গুগলের কাছে), তেমনি সেটা একটা সাইটের ক্ষতির কারণেও হতে পারে। সুতরাং আপনাকে বুঝতে হবে কোন আউটবাউন্ড লিংকটা ভালো আর কোনটা নেগেটিভ।
কীভাবে বুঝবেন সেটা?
যদি বুঝতে না পারেন, তাহলে বড় বড় অথোরিটি সাইটকে লিংক দিন। যেমন উইকিপিডিয়া, গুগল স্কলার ইত্যাদি। কারণ, যদি এমন কোনো সাইটকে লিংক দেন, যেটার পাওয়ার বা অথোরিটি আপনার সাইটের থেকে বেশি নয়; কম, তাহলে সেটা নেগেটিভ। সুতরাং বুঝতেই পারছেন, কোয়ালিটি কাউন্ট করা জরুরি।
১৮। আউটবাউন্ড লিংক রিলিভেন্সি
এটা বেশ সূক্ষ্ণ একটা বিষয়। কিন্তু জরুরি। আপনি কোন সাইটকে লিংক দিচ্ছেন সেটার উপর নির্ভর করে গুগল আপনার সাইটকে ক্যাটাগরাইজড করে ফেলছে। ব্রায়ান ডিনের মতে, যদি আপনার নিস সাইট হয় গাড়ি নিয়ে, আর আপনি আপনার সাইট থেকে একটা মুভির সাইটকে লিংক দেন; তাহলে গুগল ধরে নেবে আপনার সাইটটা অটোমোবাইল সম্পর্কিত নয়, আপনার সাইটটা হচ্ছে গাড়ি নিয়ে করা কোনো মুভি সাইট। আশা করি বিষয়টা বুঝাতে পেরেছি।
১৯। প্লাজিয়ারিজম আর্টিক্যাল
গুগলের আর্টিফিশিয়াল ইনটেলিজেন্স বট এখন খুব সহজেই বুঝতে পারে আপনার আর্টিক্যালটি অর্জিনাল নাকি কোথাও থেকে কপি/পেস্ট করে নেয়া কিংবা স্পিন কিনা। এমনকি বানান ভুল এবং গ্রামাটিক্যাল এরর বিষয়গুলোও খুব সহজে ধরতে পারে।
সুতরাং আপনাকে আর্টিক্যালের ব্যাপারে এই বিষয়গুলো অত্যন্ত সতর্কতার সাথে নিরূপন করতে হবে। অন্যথায় র্যাংক করানো একেবারেই সম্ভব হবে না।
ইদানিং অনেকে অভিযোগ করেন, তার সাইটের আর্টিক্যাল ইনডেক্স হয় না। কিংবা ইনডেক্স হয়েছিলো কিন্তু কয়েকদিন পর ডিইনডেক্স হয়ে গেছে। সম্ভাবনা ৯০% গুগল আপনার আর্টিক্যালে ডুপ্লিকেসি নির্ণয় করেছে। আর সামনে আগানোর আগেই সাইটের এক্সিসটিং আর্টিক্যালগুলোর দিকে নজর দেন। নয়তো সামনে আম এবং ছালা সবই যাবে।
২০। নোফলো-ডুফলো আউটবাউন্ড লিংক
একটা আর্টিক্যালে নোফলো এবং ডুফলো দু’ধরনের আউটবাউন্ড লিংক দেয়া উচিত। বিশেষ করে মানি আর্টিক্যালগুলোতে। কারণ এগুলো বেশ লেংথি হয়। আমি দেখেছি অনেকেই অথোরিটি আউটবাউন্ড লিংকগুলো (যেমন উইকিপিডিয়া লিংক) নোফলো করে দেন। তাহলে যেটা হয়, একটা মানি আর্টিক্যালে একটাও ডুফলো আউটবাউন্ড লিংক থাকে না।
কারণ, স্বাভাবিকভাবেই মানি আর্টিক্যালের অ্যাফিলিয়েট লিংকগুলো নোফলো হয়ে থাকে। সুতরাং এইজন্য হলেও অথোরিটি আউটবাউন্ড লিংকগুলোর অন্তত একটা ডুফলো দেবেন। দেখবেন, আপনার সাইটের চমৎকার একটা পজেটিভ রিলিভেন্সি তৈরি হয়ে গেছে।
এরকম ছোটছোট বিষয়গুলোই অন্যদের থেকে আপনার নিস সাইটকে একটু ব্যতিক্রম করে তুলবে গুগলের কাছে। এবং এই ব্যতিক্রমটা অবশ্যই পজেটিভ হিসেবেই প্রতিয়মান হবে।
নোট: এটা একটা দীর্ঘ লেখা হবে। আজকে দ্বিতীয় পর্ব লিখলাম। ইনশাআল্লাহ এই মাসের মধ্যেই বাকী পর্বগুলো লেখা শেষ করে ফেলবো। আমি যেভাবে রাফ করেছি, মোটামুটি ১০০+ হবে র্যাংকিং ফ্যাক্টর। এই ১০০টা যদি ভালো করে মনের ভেতর গেঁথে নিতে পারেন, আমি আশাবাদি এসইও নিয়ে আপনাকে আর কেউ আটকাতে পারবে না।

Excellent & most important writings I think! Best of luck for your valuable information! Very much readability!
simple and easy
alhamdulillah very helpful article, especially for beginners.
bhai waiting for part 2
Very Helpful Article
Alhamdulillah very good writing. Waiting for the next episode. Jajak Allah Khayer.May Allah give Barakah to your Business.
Thank you Bro
Hello,
If you accept guest posts, how much would you charge? What kind of content would you accept?
Stephen
I’m a random reader here , have been through lots of your articles, just wanna say , you have no idea how many you’re helping. Keep up the good work.May Allah (swt) bless you.
*how many people
thnx for your nice and informative article. Eagerly waiting for next part.
sir your article is amazing. I learned a lot from your article. And I learned many unknown things from your article. Thank you so much, sir
হেল্পফুল ছিল। অনেক উপকৃত হলাম।
Thank you so much . This article is very helpfull. I read sometime and learn more and more knowledge. So i pray for you.